Dive into the fascinating world of gizmos ionic bonds answer key, where the intricacies of ion formation unravel before your eyes. This comprehensive guide unveils the concepts of ionic bonding, showcasing how gizmos play a pivotal role in demonstrating these chemical interactions.
Embark on a journey to understand the transfer of electrons, electronegativity, and ionization energy, all while exploring the physical and chemical properties of ionic compounds. Let gizmos be your guide as you uncover the applications of ionic bonds in our everyday lives.
Ionic Bonding and Gizmos
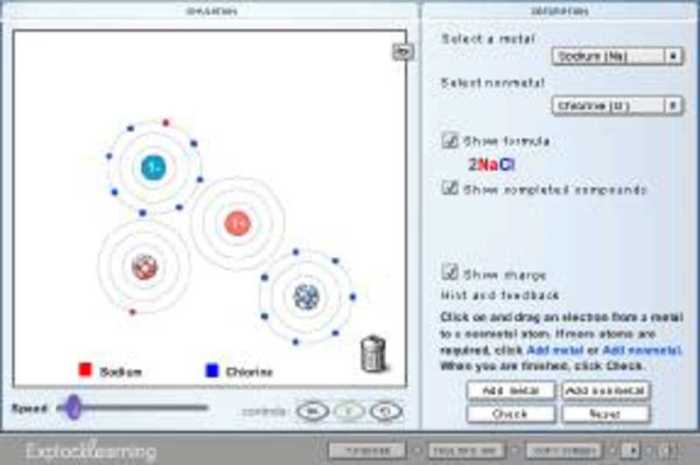
Ionic bonding is a chemical bond that involves the transfer of electrons between atoms. It occurs when one atom gives up one or more electrons to another atom. The atom that gives up electrons becomes a positively charged ion, while the atom that receives electrons becomes a negatively charged ion.
The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by the electrostatic force, forming an ionic bond.
Examples of Ionic Compounds and Their Corresponding Gizmos
Some common examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl), and calcium fluoride (CaF 2). These compounds can be represented using gizmos, which are simple diagrams that show the arrangement of atoms and ions in a molecule or compound.
If you’re looking for the gizmos ionic bonds answer key, you’re in luck! We’ve got it right here. And while you’re at it, check out our bill nye worksheet answer key as well. It’s a great resource for students who are learning about science.
With these two resources, you’ll be able to ace your next science test!
For example, the gizmo for sodium chloride (NaCl) shows a sodium ion (Na +) and a chloride ion (Cl –) arranged in a cubic lattice structure. The sodium ions are represented by small blue spheres, while the chloride ions are represented by larger green spheres.
The gizmo for potassium chloride (KCl) is similar, but the potassium ions are represented by larger purple spheres.
Gizmos and the Formation of Ionic Bonds

Gizmo is an online simulation tool that allows students to explore the formation of ionic bonds. By manipulating virtual atoms and ions, students can observe the transfer of electrons and the resulting formation of ionic compounds.
Electronegativity and Ionization Energy
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. In ionic bond formation, the more electronegative atom attracts electrons from the less electronegative atom, forming positive and negative ions.
Properties of Ionic Compounds and Gizmos
Ionic compounds exhibit distinct physical and chemical properties due to the strong electrostatic forces between their constituent ions. These properties can be explored using gizmos, interactive simulations that provide a visual representation of ionic behavior.
Physical Properties
Ionic compounds are typically hard and brittle, with high melting and boiling points. Their hardness stems from the strong electrostatic forces holding the ions in a rigid crystal lattice. The high melting and boiling points indicate the substantial energy required to overcome these forces and break apart the ionic bonds.
Ionic compounds are also good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water or melted. In these states, the ions become mobile and can carry electric current.
Chemical Properties
Ionic compounds react readily with water to form solutions. This process, known as dissolution, involves the separation of the ions and their hydration by water molecules. The resulting solution conducts electricity due to the presence of mobile ions.
Ionic compounds can also undergo chemical reactions with other ionic compounds. These reactions typically involve the exchange of ions between the compounds, resulting in the formation of new ionic compounds.
Real-World Applications, Gizmos ionic bonds answer key
Ionic compounds have numerous applications in various fields. For instance, sodium chloride (NaCl), commonly known as table salt, is essential for human and animal nutrition. Calcium carbonate (CaCO 3) is used in the production of cement and paper. Potassium nitrate (KNO 3) is employed as a fertilizer and in the manufacturing of explosives.
Gizmos for Visualizing Ionic Bonding
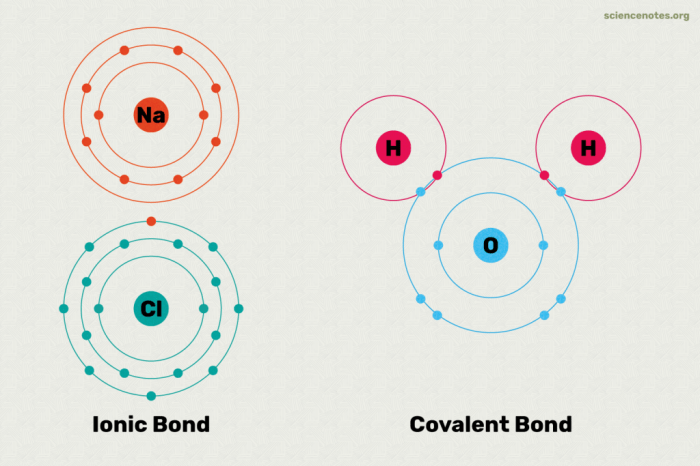
Gizmo simulations provide a dynamic and interactive way to visualize and understand the formation of ionic bonds.
Below is a table showcasing some useful Gizmos for visualizing ionic bonding, along with their descriptions, purposes, and images.
Gizmos Table
| Gizmo Name | Description | Purpose | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ionic Bonds | Allows users to create and manipulate ionic bonds between various atoms and ions. | Visualize the formation of ionic bonds and explore the properties of ionic compounds. |  |
| Ion Simulation | Simulates the behavior of ions in a solution, allowing users to observe the formation and properties of ionic bonds. | Understand the movement and interactions of ions in solution and explore the factors affecting ionic bond formation. |  |
| Ionic Solids | Visualizes the structure and properties of ionic solids, allowing users to explore the arrangement of ions in crystals. | Understand the structure and properties of ionic solids, including their electrical conductivity and melting points. | |
| Build a Model of an Ionic Compound | Provides instructions and resources for building a physical model of an ionic compound. | Hands-on experience in constructing an ionic compound model and understanding the arrangement of ions. |  |
Clarifying Questions: Gizmos Ionic Bonds Answer Key
What is ionic bonding?
Ionic bonding is a chemical bond formed between two oppositely charged ions, resulting from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
How do gizmos help in understanding ionic bonding?
Gizmos provide interactive simulations and visualizations that demonstrate the formation of ionic bonds, allowing students to observe the transfer of electrons and the resulting ion charges.
What are some examples of ionic compounds?
Common examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium iodide (KI), and calcium oxide (CaO).